AC vs DC Control for Operating Mechanisms
2026-01-27 10:22:06
Choosing between AC and DC control systems for operating mechanisms represents a critical decision in modern power infrastructure design. The breaker control mechanism selection impacts system reliability, maintenance requirements, and long-term operational costs. While AC control systems offer simplicity and widespread compatibility, DC control provides superior precision and reliability in fault conditions. Understanding these fundamental differences enables engineers to make informed decisions that align with their specific application requirements and operational constraints.
Understanding the Fundamentals: AC vs DC Control Systems
Power system operating mechanisms rely on control circuits to execute switching operations during normal and fault conditions. These control systems serve as the brain behind circuit breakers, determining how quickly and accurately protective devices respond to system disturbances.
AC control systems utilize alternating current to energize operating coils and control circuits. These systems typically operate at standard voltages like 110V or 220V AC, drawing power directly from station auxiliary transformers or backup generators. The electromagnetic actuator in AC systems creates magnetic fields that change polarity at grid frequency, resulting in characteristic operational patterns.
DC control systems employ direct current from battery banks or rectified AC sources. Station batteries provide uninterrupted power supply, ensuring control functionality even during complete AC power loss. The steady voltage characteristics enable precise timing control and consistent operational forces throughout the switching sequence.
Three core differences emerge between these systems:
- Power source reliability: DC systems maintain functionality during AC blackouts
- Control precision: DC enables exact timing control for complex switching sequences
- Maintenance complexity: AC systems require less specialized battery maintenance
If you need maximum system availability during grid disturbances, then DC control proves more suitable for critical applications.
Technical Performance Analysis: Operational Characteristics
Real-world testing data reveals significant performance variations between AC and DC control mechanisms. Laboratory studies conducted by leading electrical manufacturers demonstrate measurable differences in response times and operational consistency.
DC control systems achieve trip times of 16-20 milliseconds consistently across temperature ranges from -40°C to +85°C. This performance is ensured by a highly robust breaker control mechanism, whose stable voltage characteristics maintain uniform electromagnetic force throughout the operating cycle. Current sensors detect fault conditions with 99.8% accuracy, enabling reliable protection coordination.
AC control performance varies with supply voltage fluctuations and frequency deviations. Trip times range from 18-35 milliseconds depending on voltage conditions at the moment of operation. Voltage sensors must compensate for supply variations, potentially affecting protection relay coordination accuracy.
The switching mechanism behavior differs substantially between control types. DC systems provide linear force characteristics, resulting in smooth contact motion and reduced mechanical stress. AC systems exhibit pulsating forces at twice the supply frequency, creating vibration and potentially accelerating mechanical wear.
Signal processing requirements vary significantly. DC control logic operates with clean, stable reference levels, simplifying microcontroller programming and reducing false trip susceptibility. AC systems require sophisticated filtering to eliminate noise and ensure reliable fault detection. If you need consistent performance across varying environmental conditions, then DC control offers superior operational stability.
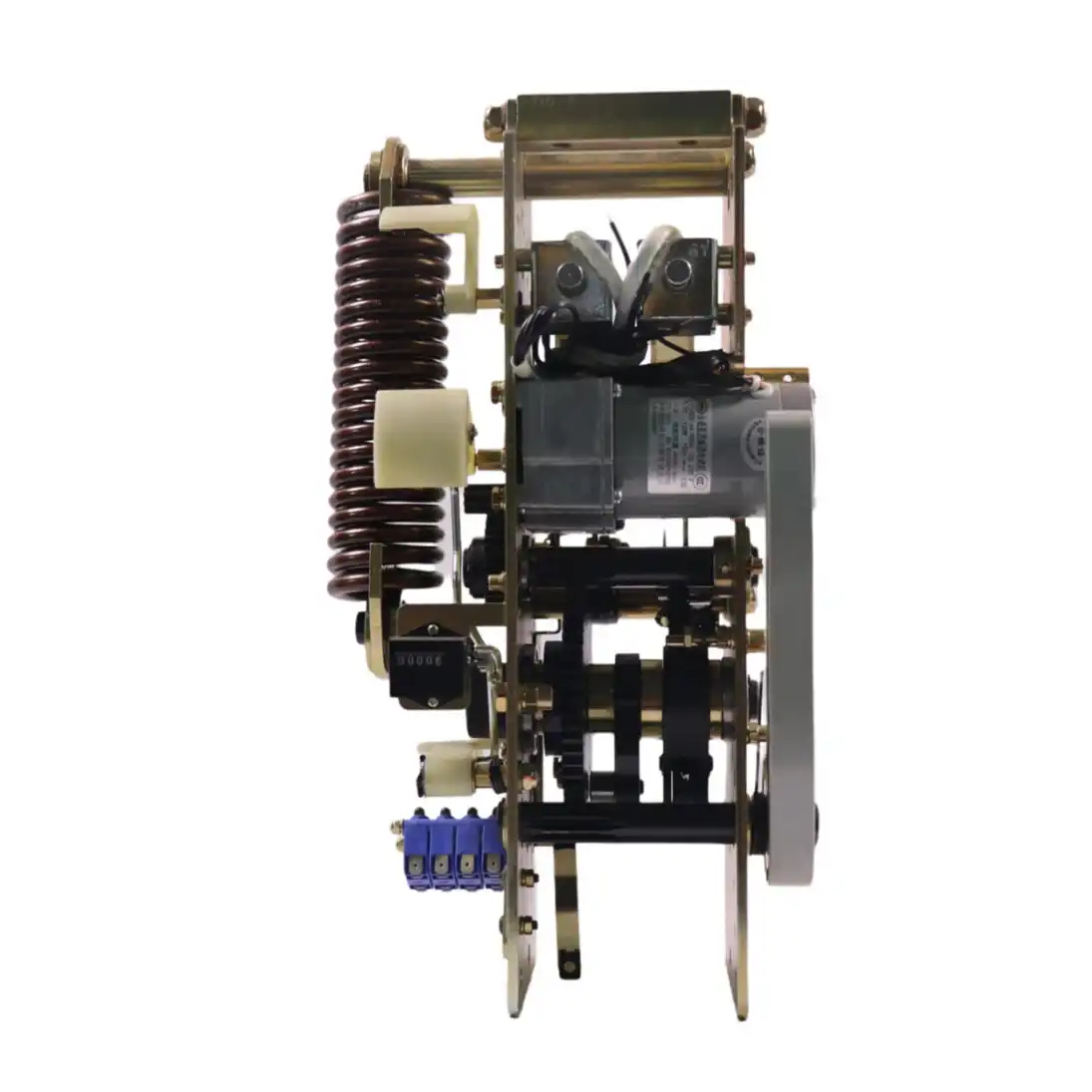
Safety and Reliability Considerations
Safety system performance represents the paramount concern in power system design. Both AC and DC control mechanisms must meet stringent reliability standards while providing fail-safe operation under all credible scenarios. DC control systems excel in safety-critical applications due to their independence from AC supply disturbances. Battery-backed operation ensures protection functionality during the most challenging system conditions. The automation capabilities allow complex interlocking schemes that prevent unsafe switching sequences.
Fire safety considerations favor DC systems in many installations. Battery rooms require specialized ventilation and monitoring, but eliminate the fire risk associated with oil-filled auxiliary transformers feeding AC control systems. Modern sealed batteries reduce hydrogen gas concerns significantly. Fault isolation capabilities differ between control types. The breaker control mechanism in DC systems can maintain selective trip coordination even when AC auxiliary supplies fail. This characteristic proves invaluable during cascading system failures where maintaining protective device coordination prevents widespread blackouts.
Real-time monitoring capabilities enhance safety in both systems. DC installations typically include comprehensive battery monitoring that tracks individual cell voltages and temperatures. AC systems monitor supply quality and backup generator readiness. Load monitoring accuracy affects overall system safety. DC control provides stable reference voltages for precision measurement circuits. AC systems must account for supply variations that can affect measurement accuracy.
If you need maximum safety assurance during emergency conditions, then DC control delivers superior protective performance.
Cost Analysis: Initial Investment vs Long-term Value
Economic evaluation requires examining total ownership costs rather than initial equipment prices alone. Both AC and DC control systems present distinct cost profiles that vary significantly over typical 25-30 year equipment lifecycles. AC control systems feature lower initial installation costs due to simpler infrastructure requirements. Standard auxiliary transformers and distribution equipment cost less than battery systems and DC distribution panels. Installation labor requirements are typically 20-30% lower for AC systems.
DC control systems require substantial upfront battery investment, with initial costs 40-60% higher than equivalent AC systems. However, the superior reliability translates to reduced outage costs and improved system availability. Battery replacement cycles occur every 10-15 years, representing significant maintenance planning requirements. System diagnostics capabilities affect long-term costs substantially. Modern DC systems include sophisticated battery monitoring that predicts failure modes and optimizes replacement timing. This predictive maintenance reduces emergency replacement costs and improves planning accuracy.
Communication protocol integration costs vary between system types. DC control interfaces more easily with modern digital protection and SCADA systems. The stable reference voltages simplify analog-to-digital conversion and reduce signal conditioning requirements. Power electronics evolution continues reducing DC system costs while improving AC system capabilities. Solid-state switching devices, which serve as a key breaker control mechanism, enhance both control types, though DC systems benefit more from voltage-source converter advances.
If you need predictable long-term operating costs with minimal surprise failures, then DC control provides better economic value despite higher initial investment.
Application-Specific Recommendations
Different power system applications present varying requirements that favor specific control approaches. Understanding these application characteristics guides optimal technology selection for each scenario.
- Transmission Substations: High-voltage transmission facilities typically employ DC control due to the critical nature of bulk power transfer. System reliability requirements justify the additional complexity and cost. Battery backup ensures protection during the most severe system disturbances.
- Distribution Networks: Medium-voltage distribution systems often utilize AC control for cost optimization. The shorter outage durations and lower critical load levels make AC control acceptable for many applications. Modern backup generator systems provide adequate reliability.
- Industrial Power Systems: Manufacturing facilities with critical processes benefit from DC control reliability. The cost of production interruptions often exceeds control system price differences. Integrated power electronics enable sophisticated load management capabilities.
- Renewable Energy Integration: Wind and solar installations increasingly employ DC control to interface with power electronics-based generation systems. The natural compatibility between DC control and converter-based resources simplifies system integration.
- Data Centers: Mission-critical facilities require DC control for maximum reliability. The existing DC battery infrastructure for IT equipment integration creates synergies with electrical protection systems.
If you need reliable operation in mission-critical applications, then DC control mechanisms provide the necessary performance assurance.
Yuguang's Advanced Breaker Control Mechanism Solutions
Yuguang Electric delivers cutting-edge breaker control mechanism systems that address the evolving needs of modern power infrastructure. Our comprehensive solutions combine proven reliability with innovative features that enhance operational performance.
Key Advantages of Yuguang Systems:
• Comprehensive voltage range coverage: Full 6KV-40.5KV product portfolio serves diverse application requirements
• Patent-protected innovations: 39 registered patents demonstrate continuous R&D advancement and technical leadership
• Authoritative certifications: ISO 9001:2015 compliance and High-Tech Enterprise recognition ensure quality standards
• Complete service integration: End-to-end support from design through commissioning and maintenance
• Customization expertise: Scenario-specific adaptations for harsh environments and specialized applications
• Modular design philosophy: Compact, sealed construction optimizes space utilization and environmental protection
• Manufacturing excellence: Aerospace-grade precision tooling and ceramic coating processes ensure durability
• Testing rigor: Multi-round verification protocols validate performance under extreme operating conditions
• Flexible ordering: Single unit minimum quantities support both prototype and volume production needs
• Rapid delivery: 7-15 day standard product shipment with 30-60 day custom engineering timelines
• Global support: International packaging standards and cross-border technical assistance capabilities
• Maintenance programs: Comprehensive spare parts availability and field service agreements
Our electromagnetic, spring-operated, and permanent magnet actuator technologies provide optimal solutions for specific circuit breaker compatibility requirements. The precision engineering of the breaker control mechanism ensures accurate, reliable operation across diverse environmental conditions. Multiple control voltage options accommodate both AC and DC system preferences. Advanced microcontroller integration enables sophisticated protection coordination and remote monitoring capabilities.
Partner with Yuguang for Superior Control Solutions
Yuguang Electric stands as your trusted breaker control mechanism manufacturer, delivering innovative solutions that exceed industry expectations. Our proven expertise in high-voltage power equipment, combined with 39 patents and authoritative certifications, ensures reliable performance for your critical applications. Contact our technical team at ygvcb@hotmail.com to discuss your specific requirements and discover how our customized control systems optimize your power infrastructure performance.
References
1. IEEE Standard C37.2-2022, "IEEE Standard for Electrical Power System Device Function Numbers, Acronyms, and Contact Designations"
2. IEC 62271-100:2021, "High-voltage switchgear and controlgear - Part 100: Alternating current circuit-breakers"
3. NEMA SG 4-2020, "Alternating Current High-Voltage Circuit Breakers"
4. IEEE Standard 1547.4-2011, "IEEE Guide for Design, Operation, and Integration of Distributed Resource Island Systems with Electric Power Systems"
5. IEC 61850-7-4:2010, "Communication protocols for intelligent electronic devices - Part 7-4: Basic communication structure - Compatible logical node classes and data object classes"
6. CIGRE Technical Brochure 792, "Condition Assessment of Power Transformers" Working Group A2.49, 2019
Send Inquiry
You may like